Application Structure
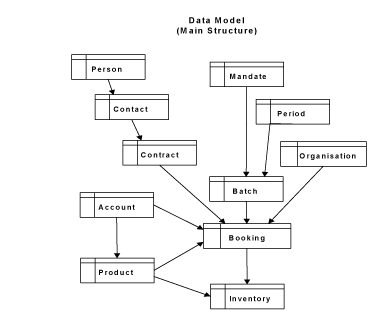
sqlFinance uses a well proven data model. User specific data structures can be added to the basic data model. After specification of new data structures in the meta database, the form manager will support presentation and update operations on these data structures as well. Through master detail and lookup relastionships new tables may be integrated into the sqlFinance data model. The high consistency of the data model keeps database structure simple and is a solid base for queries and later analysis.
sqlFinance can be combined with Business Process Engineering for the modeling of the following basic dimensions:
- WHERE: Company Organisation (cost center)
- WHAT: Product.or Service
- WHO: Contractor (client, vendor, employee)
- WHEN: Period (reporting period, closing period, order date, due date)
- WHY: Business (tracking of business fields and profitability)
Technical features of server version:
- Multiuser Environment
- Transaction processing
- Mutliuser acces control
- Record level locking
- Locking of closed periods amd closed batches
- Log file for follow up of user activities
Basic application elements
- Accounts (chart with IFRS sample, account structure, reporting account structure, account groups)
- Company and company organisation (profit centers, cost centers, groups within the organisation)
- Contracts (orders, sales, banks, insurances, employment) with contract financial status (earnings, expenses, balance, credit limit), contract specific properties (currency, taxability, market region) and contact person/adress.
- Products (including bill of materials, product line with instructions for general ledger accounting and tax management)
- Prices and discounts (per market, company, product line or product). Price list per market, with foreign currency. Price per unit of measure, per minimum quantity. Special prices and discount sales.
- Properties (descriptive feature for persons, positions, batches)
- Batches with collection of bookings (ex. General Ledger batch with closing records, Sales Order batch with sales items for a customer)
Batch structure
- General Ledger (multiline entries, foreign currency)
- Accounts Receivable/Payable (conditions, adress information, foreign currency, payment clearing)
- Purchase and Sales: (product, unit of measure, price, discount, tax, sales person, time status, foreign currency)
- Payroll (labor costs, labor quantity, organisation, insurance and social security, percentages, accounting information)
- Time Management (time, price, contract, employee)
- Portfolio Management (value, price, expenses)